As the digital landscape evolves with increasing threats, organizations are now adopting the principles of Zero Trust Security. Trust is no longer presumed but role-based and verified at every step in this era. In this blog, we will delve deeper into the significance of Zero Trust Security, exploring its core principles for 2024 to gain a comprehensive understanding of its importance in modern cybersecurity.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust represents a transformation in the IT security model, requiring strict identity verification for every user accessing resources on a private network. Unlike the traditional “Trust but Verify” approach, it prioritizes “Never Trust, always verify.” Continuous verification within the internal network mitigates the risk of outsiders breaching sensitive organizational information.
In contrast to the traditional model securing network perimeters, Zero Trust overrides default trust within the network. This model is especially essential in today’s landscape, where data spans multiple cloud vendors, challenging the efficacy of centralized security controls. Zero Trust mandates verification from every entity seeking network access, providing a critical security layer proven to prevent data breaches. Given the average cost of a breach reaching $4.35 million, organizations increasingly recognize the need for a zero-trust security policy to protect their assets effectively.
Zero Trust Architecture Explained
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a revolutionary framework transcending the limitations of traditional security models. It adopts a data-centric approach, departing from the conventional network-centric focus. Zero Trust architecture utilizes least-privileged access controls and rigorous user authentication. Unlike traditional models relying on assumed trust, Zero Trust enhances cyber threat defense.
Zero Trust directs access policies based on dynamic context—considering user roles, location, device, and requested data—effectively preventing unauthorized access and lateral movement within an environment. This architectural shift enhances the ability to prevent modern cyber threats, offering a more resilient and adaptive security posture. With ZTA, organizations gain a comprehensive defense mechanism that aligns with the evolving digital landscape.
Core Principles of Zero Trust Model
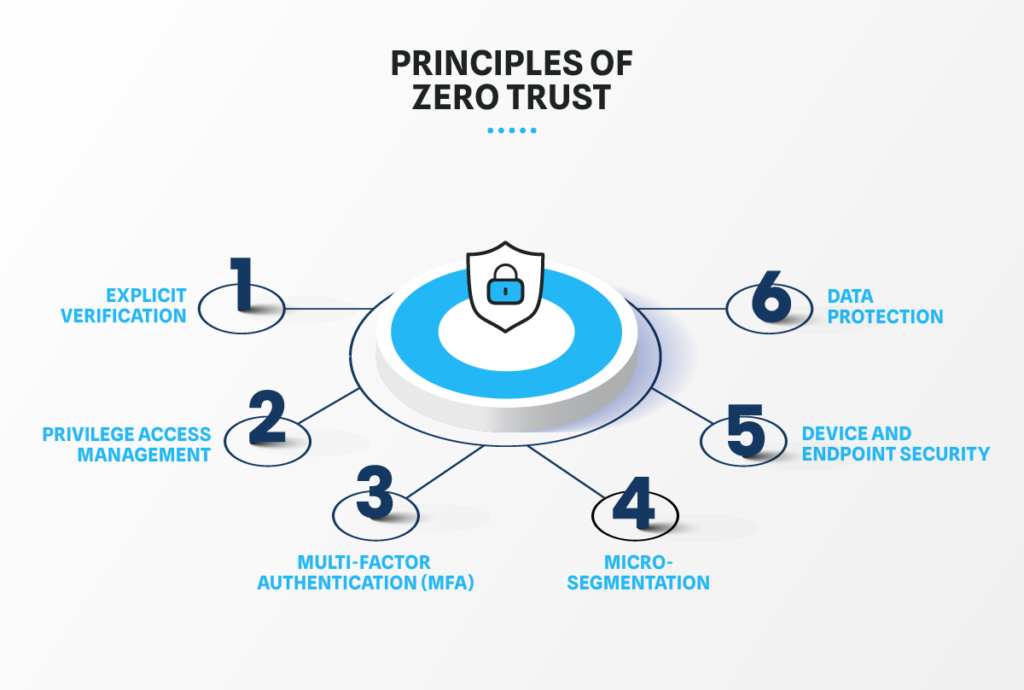
Zero Trust Security is founded on a series of core principles that drive its implementation and effectiveness. Understanding these zero trust principles is crucial to know how this model fundamentally alters the traditional security approach.
- Verify Explicitly: Every access request is authenticated and authorized based on all available data points, including user identity, location, device health, and data sensitivity. This continuous verification ensures that only legitimate users can access resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Least Privilege Access: Users are given the minimum access levels necessary to perform their tasks. This principle reduces the potential damage from compromised accounts and limits access to sensitive data and systems. It also ensures tighter control over user permissions.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): To add an extra layer of security, multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to verify their identity using two or more authentication factors. This approach significantly enhances authentication security and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access.
- Micro-Segmentation: The network is divided into smaller segments, each with its security controls. It reduces the attack surface and limits attackers’ lateral movement within the network, making it harder for threats to spread.
- Device and Endpoint Security: Every device that connects to the network is considered untrusted until verified. Continuous monitoring and management of devices ensure they comply with security policies, protecting the network from potentially compromised devices.
- Data Protection: Safeguarding data at rest and in transit is a critical aspect of Zero Trust. Encryption, data loss prevention (DLP), and other data protection techniques secure sensitive information and ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a critical component of the Zero Trust model that provides secure access to applications and services based on strict identity verification and context. Unlike traditional VPNs, which grant access to an entire network, ZTNA restricts access to specific resources, thus minimizing the attack surface.
ZTNA solutions work by creating secure tunnels between the user and the requested resource, authenticating each session individually. This approach ensures that even if a user’s credentials are compromised, the attacker cannot gain broad access to the network.
How to Implement Zero Trust ?
Implementing Zero Trust security model involves several strategic steps that organizations must follow to ensure a successful transition from traditional security models.
1. Identity Verification and Authentication:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users accessing resources.
- Utilize robust authentication methods such as biometrics, smart cards, or hardware tokens.
- Integrate with identity providers (IdPs) that support modern authentication protocols like OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect.
2. Identity Governance and Administration (IGA):
- Establish policies and procedures for provisioning and de-provisioning user access.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure users only have access to the resources necessary for their roles.
- Regularly review and audit user access rights to ensure compliance and security.
3. Identity Federation:
- Implement identity federation to enable single sign-on (SSO) across different applications and services.
- Utilize standards like Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) or OAuth 2.0 for federated authentication.
- Ensure proper configuration and regular updates of federated authentication settings.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Risk Assessment:
- Monitor user behavior and access patterns for anomalies that may indicate potential security threats.
- Implement user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to detect suspicious activities.
- Conduct regular risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential security risks associated with user identities.
5. Privileged Access Management (PAM):
- Implement strict controls and monitoring for privileged accounts.
- Utilize just-in-time (JIT) privilege elevation to limit the duration of elevated access.
- Implement session monitoring and recording for privileged sessions.
6. Device Identity and Access Control:
- Implement device authentication and validation to ensure only trusted devices can access resources.
- Utilize mobile device management (MDM) solutions to enforce security policies on devices accessing corporate resources.
- Regularly update and patch devices to maintain security compliance.
7. Network Segmentation and Micro-Segmentation:
- Implement network segmentation to isolate sensitive resources from the rest of the network.
- Utilize micro-segmentation to enforce granular access controls within the network based on user identity and context.
- Continuously monitor and adjust segmentation policies to adapt to changing threats.
8. Data Protection and Encryption:
- Implement data encryption for sensitive data at rest and in transit.
- Utilize data loss prevention (DLP) solutions to prevent unauthorized access and exfiltration of sensitive data.
- Regularly review and update encryption protocols and DLP policies.
9. User Education and Awareness:
- Provide regular training and awareness programs to educate users about best practices for security and the importance of protecting their credentials.
- Encourage users to report any suspicious activities or security incidents promptly.
- Develop and distribute clear guidelines on secure password management and phishing awareness.
10. Compliance and Governance:
- Ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc.
- Establish clear governance policies and procedures for identity and access management processes.
- Regularly audit and update compliance measures to align with evolving regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Zero Trust Model
Adopting Zero Trust Security brings numerous benefits to organizations, enhancing their overall cybersecurity posture:
- Enhanced Security: Zero Trust significantly reduces the risk of security breaches by eliminating implicit trust and continuously verifying every access request.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Micro-segmentation and strict access controls limit the areas attackers can target, minimizing potential damage.
- Meet Compliance: Zero Trust helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by ensuring robust data protection and access control measures.
- Improved User Experience: While Zero Trust may seem restrictive, it improves user experience by enabling secure, seamless access to applications and resources from any location.
- Cost Savings: Given the high costs associated with data breaches, preventing breaches, and minimizing their impact can lead to substantial cost savings.
Choose AuthX for Zero Trust Security
Adopting Zero Trust with AuthX is not just a security enhancement: it’s a strategic move towards a more secure and resilient future. AuthX is a leader in providing comprehensive Zero Trust solutions tailored to your organization’s unique needs. Through our open standards-based platform, AuthX seamlessly integrates with other modern identity governance, lifecycle, networking, and security solutions. This ensures a cohesive and unified security strategy that leverages your existing investments and enhances your overall security posture.
Our security offerings include advanced identity and access management, passwordless multi-factor authentication (featuring innovative modalities like Badge Tap & Go, Mobile Push, Biometrics, and more), and robust endpoint security measures designed to protect your critical assets.
By partnering with AuthX, you can effortlessly transition to a zero-trust model, bolstering your defense against modern cyber threats. Our experts will guide you through every implementation step, helping you establish a secure, adaptable, scalable security framework.
FAQs
What is a Zero Trust Network?
What technologies enable Zero Trust security?
What are the key principles of Zero Trust?
There are mainly six zero trust principles:
Verify Explicitly
Least Privilege Access
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Micro-Segmentation Device
Endpoint Security Data Protection
How does Zero Trust security work?
Zero Trust security works with the basic principle of “never trust, always verify”, by treating every user/device/application as untrusted, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network. It rigorously verifies and authenticates each access request using multiple authentication factors.
What are the benefits of implementing a Zero Trust Framework?
The main benefits include:
Reduces data breach risks through constant verification Limits user access to critical resources Monitors all activity for faster threat detection Helps meet compliance requirements Works well with any network setup
What is the difference between Zero Trust and a VPN?
A VPN is like having a private tunnel that will allow you to safely connect to your company’s network from home or anywhere. But, Zero Trust works differently. Zero Trust checks who you are and if your device is safe every time when you try to access anything.

















