Businesses often say, “We’ve secured our logins! What else do we need?” The reality is that logging in is only the beginning of the security equation. User behavior can change mid-session, devices can be compromised, as cybercriminals are getting smarter daily.
This is where continuous authentication steps in. Unlike traditional login methods that verify identity just once, continuous authentication monitors user behavior, device signals, and other contextual factors in real-time to ensure security doesn’t stop at the door. It is no longer about who logs in; it is about who stays in.
What is Continuous Authentication?
Continuous authentication is a dynamic security process that validates user identity throughout a session. Instead of a “set it and forget it” model where identity checks happen once at login, continuous authentication keeps a watchful eye, assessing real-time behavioural patterns, device posture, and even environmental factors like geolocation or network changes.
Think of it like this: traditional authentication is like checking a guest’s ID when they enter a building. Continuous authentication is like discreetly monitoring their behaviours to ensure they belong there the whole time.
When talking to IT leaders about this, we often hear, “How much of a difference can mid-session monitoring make?” The answer is an enormous difference. Continuous authentication addresses threats after login—think stolen sessions, device takeovers, or insider threats.
How Continuous Authentication Works?
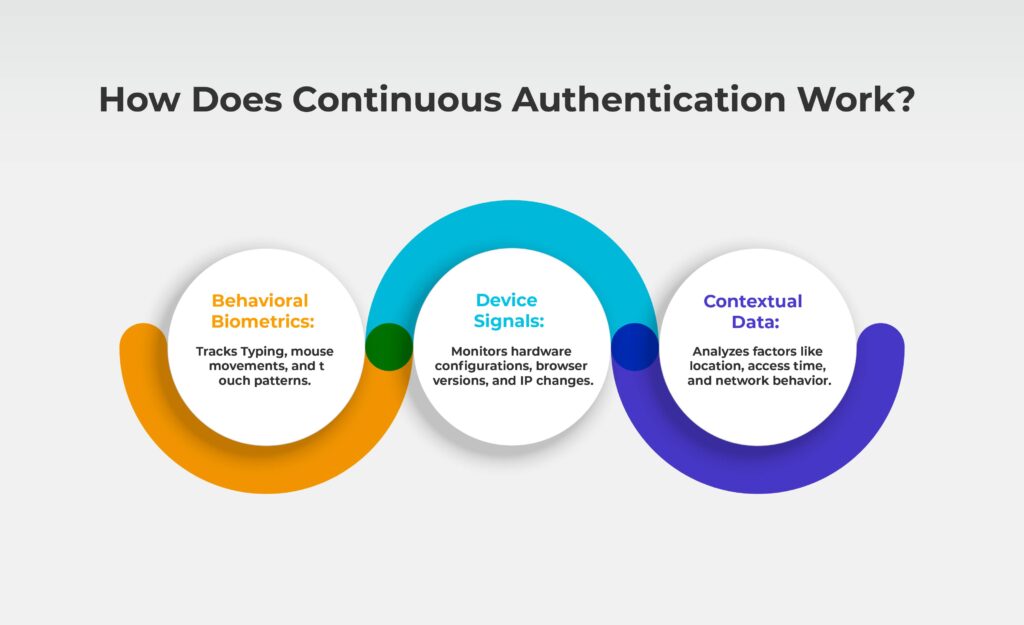
Continuous authentication relies on a mix of technologies to analyze:
- Behavioural Biometrics: Mouse movements, typing speed, and touchscreen patterns.
- Device Signals: Hardware changes, browser versions, and IP addresses.
- Contextual Data: Location, time of access, and network behaviour.
For example, red flags are raised if a user logs in from their office but suddenly starts performing sensitive actions from a different country or their typing rhythm seems off. This isn’t about locking users unnecessarily but making intelligent, real-time decisions to verify ongoing trust.
This makes it even more powerful: continuous authorization works hand-in-hand with authentication to assess what the user is doing mid-session. If suspicious behaviour is detected, access permissions can adjust automatically like restricting downloads or turning off certain features.
3 Types of Authentications
To understand the need for continuous authentication, let’s quickly revisit the 3 types of authentication businesses rely on today:
- Static Authentication: This is the most familiar method—usernames, passwords, and even MFA codes. It validates identity once at login but stops there.
- Adaptive Authentication: Risk-based authentication uses context, such as location or device health, to determine if extra verification is needed.
- Continuous Authentication: The most advanced form of identity verification happens continuously during a user session. It ensures ongoing trust without disrupting the user experience.
In many industries, businesses rely solely on static methods. But as cyber risks evolve, it’s becoming clear that static checks are outdated. Continuous authentication is a leap forward—it evolves as users do.
Benefits of Continuous Authentication
So, why is continuous authentication a game-changer? Here are three key benefits:
- Prevents Mid-Session Threats: Static authentication leaves a massive blind spot between login and logout. Continuous authentication fills that gap, detecting anomalies as they happen.
- Reduces Reliance on Static Credentials: Passwords can be shared, stolen, or phished. Continuous authentication shifts the focus to behaviours and real-time patterns, making it much harder for attackers to bypass.
- Enhances User Experience: Security shouldn’t come at the cost of usability. Continuous authentication happens in the background, allowing users to work seamlessly unless something suspicious is flagged.
Use Cases for Continuous Authentication
Where does continuous authentication make the most significant impact? Here are a few examples:
- Financial Services: Banks use continuous authentication to monitor for fraudulent behaviour during sensitive financial transactions. For example, a sudden change in typing cadence might indicate that a fraudster has taken control.
- Healthcare: Protecting electronic health records (EHRs) requires ongoing validation—especially as doctors and nurses move between devices or locations throughout the day.
- Remote Workforces: With employees accessing systems from anywhere, continuous authentication ensures that unauthorized access doesn’t last long, even if a laptop or login is compromised.
AuthX's Continuous Authentication Solution
At AuthX, robust security comes from layers of intelligent protection. Our platform combines all types of authentications—static, adaptive, and continuous—into a seamless, user-friendly experience.
Here’s what makes AuthX’s solution stand out:
- Behaviour-Based Monitoring: Tracks and analyzes user actions without disrupting workflows.
- Real-Time Authorization: Combines continuous authorization with risk-based policies to adapt access permissions instantly.
- Passwordless Authentication: Reduces reliance on static credentials through biometrics, mobile push notifications, and more.
We understand that security and user experience must be integrated. That’s why AuthX ensures ongoing trust with minimal friction.
Conclusion
Continuous authentication isn’t just a “nice-to-have” anymore—it’s essential for any business looking to stay ahead of modern threats. Monitoring users throughout their session closes critical security gaps, stops mid-session attacks, and gives IT teams the confidence to trust their systems.
If you can see how continuous authentication can elevate your security posture, AuthX is here to help. Contact us to learn how we can keep your workforce secure beyond the login.


