In an era dominated by digital advancements, ensuring organizational security is essential. Traditional authentication methods like passwords have proven susceptible to various security breaches. In response to these security threats, Biometric Authentication has emerged as a reliable solution, utilizing unique physiological and behavioral traits for identity verification.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric Authentication involves using an individual’s unique biological characteristics to confirm their identity. Unlike traditional methods that rely on something the user knows (like a password) or something they have (like a security token), biometric Authentication is based on something they are. This approach eliminates the probability of errors in user verification and offers a more secure and user-friendly way to access devices, systems, and sensitive information through biometric identification.
Types of Biometric Authentication Methods
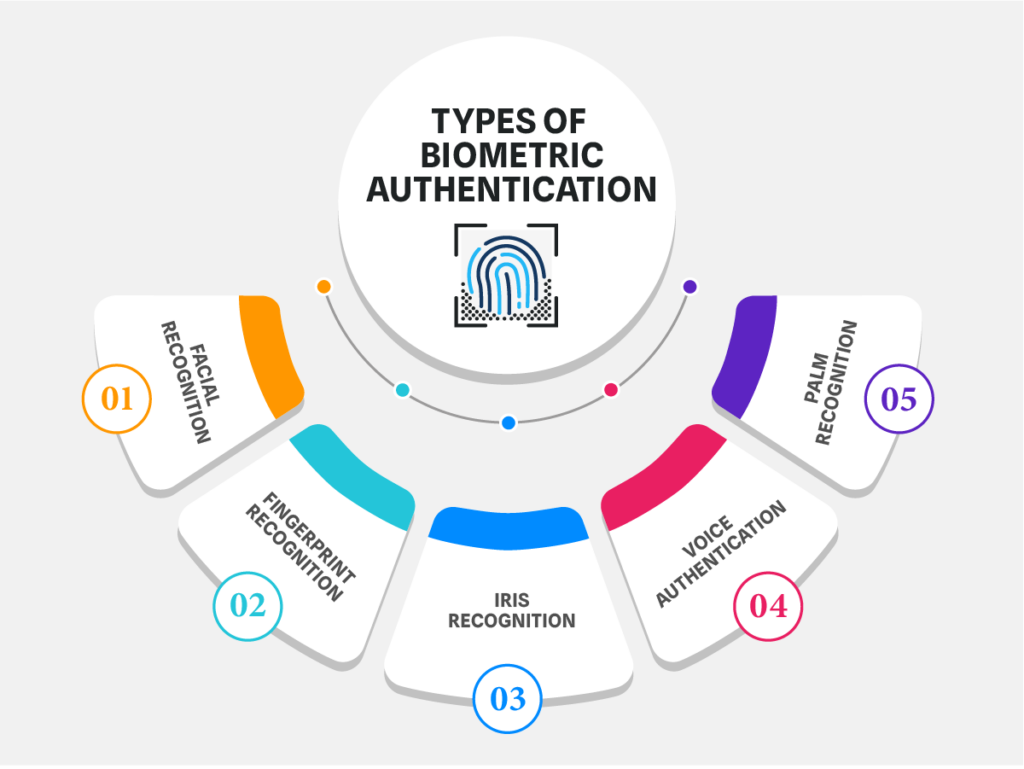
- Facial Recognition: Facial recognition technology analyzes facial features and patterns to identify individuals. This method has gained widespread popularity, with applications ranging from unlocking smartphones to enhancing airport security. The system captures and compares key facial elements, ensuring a high level of accuracy in identification.
- Fingerprint Recognition: Fingerprint scanning is one of the oldest and most established forms of biometric Authentication. Every individual possesses a unique fingerprint, and modern fingerprint scanners use sensors to capture and analyze the minutiae points of a fingerprint for precise identification.
- Iris Recognition: Iris authentication focuses on the unique patterns within the iris of the eye. The intricate and complex structure of the iris makes it an ideal biometric identifier. Iris recognition systems use advanced cameras to capture high-resolution images of the iris, which are then analyzed to verify identity.
- Voice Authentication: Voice biometrics authentication relies on an individual’s distinct vocal characteristics. The system examines different elements of the voice, including pitch, tone, and cadence, to generate a distinctive voiceprint. Voice authentication is widely used for telephone-based services and can be an effective method for remote Authentication.
- Palm Recognition: Palm recognition involves capturing and analyzing the unique patterns and features of an individual’s palm. The palm’s veins, lines, and contours create a distinctive biometric profile. This method is beneficial when environmental factors may make fingerprint recognition challenging.
What is Multimodal Biometric Authentication?
Recognizing the need for heightened security, many organizations are adopting multimodal Authentication. This approach combines multiple secure biometric methods, such as facial and voice recognition or fingerprint and iris recognition. Multimodal Authentication adds an extra layer of complexity, making it even more challenging for malicious actors to compromise security. Multimodal Authentication enhances accuracy and addresses scenarios where a single biometric method may face limitations, such as environmental factors affecting facial recognition. Additionally, multimodal systems can dynamically adjust the authentication process based on user context, improving overall safety.
Advantages of Biometric Authentication
- Restricted Access: Biometric Authentication ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information or secure locations. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and protects against identity theft.
- Enhanced Security: Biometric authentication methods offer a higher level of security than traditional methods. The unique nature of biometric traits makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized users to replicate or forge them.
- Minimizes Human Error: Unlike passwords that can be forgotten, lost, or shared, biometric Authentication relies on innate and unique characteristics. This minimizes the likelihood of human error in authentication processes, leading to a more reliable and efficient system.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While implementing biometric authentication systems may involve an initial investment, the long-term cost-effectiveness is undeniable. Reducing security breaches, password resets, and administrative overhead contributes to cost savings.
- Fraud Detection: Biometric authentication systems often include advanced features for fraud detection. For example, facial recognition systems may incorporate liveness detection to ensure that a live person is presenting their face, preventing the use of photographs or videos for unauthorized access.
Passwords Vs. Biometrics: Which One is Stronger?
Comparing traditional passwords and biometric authentication methods is crucial for understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each. While passwords have been a standard means of securing accounts, they are exposed to various vulnerabilities, such as brute force attacks, password sharing, and forgetting. On the other hand, biometric Authentication offers a more secure and user-friendly alternative that relies on unique physiological or behavioral traits. Biometric security eliminates the need for users to remember complex passwords, reducing the risk of human error. The inherent uniqueness of biometric data makes it highly challenging to access unauthorized data, providing a more robust defense against security breaches than traditional passwords. It also enhances user satisfaction by offering passwordless Authentication.
Embrace Biometric Authentication!
Biometric Authentication Myths Busted:
Myth 1: Biometric data can be easily hacked.
Reality: The user's biometric data is securely stored and encrypted, making hacking challenging. Additionally, advanced systems incorporate liveness detection to prevent the use of fake or replicated biometric data.
Myth 2: Biometric systems are error prone.
Reality: While no system is perfect, biometric Authentication has significantly lower error rates than traditional methods. Continuous advancements in biometric authentication technology continue to improve accuracy and reliability.
Myth 3: Biometric data is not private.
Reality: Biometric data is typically stored in a secure and encrypted format. Moreover, modern systems often use templates derived from biometric features rather than storing raw data, further safeguarding privacy.

Biometric Authentication Use Cases:
Biometric Authentication finds applications across various industries and scenarios:
- Banking and Finance: Banks and financial institutions use Biometrics to enhance the security of online transactions and account access. Moreover, Biometrics helps prevent identity theft and fraud by verifying the user’s identity through unique biological traits. Additionally, Biometrics streamlines customer verification processes, reducing the reliance on passwords and PINs.
- Healthcare: Biometric systems secure patient data and control access to sensitive medical records, ensuring confidentiality. They enable accurate patient identification, reducing medical errors and improving patient care. Biometrics also facilitates compliance with healthcare regulations by ensuring that only authorized personnel can access specific information.
- Government: Biometrics are employed for citizen identification, border control, and secure access to government facilities. Additionally, they play a crucial role in national security by accurately identifying individuals and preventing illegal entry. Governments also use Biometrics for efficient and secure e-governance services, providing citizens with easy access to public services.
- Retail: Biometric Authentication is used in retail for secure point-of-sale transactions and access control to restricted areas. It enhances the customer experience by enabling fast and secure fingerprint or facial recognition payments. Retailers also utilize biometric information to manage employee attendance and secure access to inventory storage areas.
- Education: Educational institutions utilize biometric technology for student identification and secure access to campus facilities. Biometrics streamlines attendance tracking, ensuring accurate and efficient record-keeping. Additionally, they enhance campus security by controlling access to dormitories, labs, and other sensitive areas.
Conclusion
Robust and secure authentication methods are becoming increasingly critical in these modern times. Therefore, use Biometric Authentication for a highly effective solution with diverse facial, fingerprint, iris, voice, and palm recognition techniques. Moreover, with its inherent advantages and adaptability, Biometrics is a crucial element in ensuring the security and protection of personal information.
AuthX is a notable player in Biometric Authentication, offering practical solutions that prioritize security and user convenience. With expertise in facial recognition and fingerprint authentication, AuthX ensures reliable identity verification without unnecessary intricacies. The smooth integration of these biometric methods enhances Authentication, fostering a more secure digital experience. If you’re interested in customized solutions for your business needs, connect with our experts to explore how AuthX can meet your requirements effectively.
FAQs
How does biometric authentication work?
Biometric systems capture specific data from an individual’s physical traits (e.g., a fingerprint scan or facial image) and convert it into a digital template. When you attempt to authenticate, the system compares your captured data with the stored template to confirm your identity.
How does biometric authentication work?
Following are a few of the common types of biometric authentication:
- Fingerprint recognition
- Facial recognition
- Iris recognition
- Voice recognition
- Retina scan
- Palm print recognition
Is biometric authentication secure?
Biometric authentication is more secure than traditional passwords or PINs as it relies on unique, inherent characteristics. However, security can be compromised if your biometric data falls into someone’s hands. This is where Multi-Factor Authentication plays an important role.
What are the advantages of biometric authentication?
Convenience: Need not remember passwords
Accuracy: A person has unique features that cannot be replicated easily.
Speed: Generally, quicker than manual methods (such as entering a PIN).
Lower risk of fraud: More difficult for someone to impersonate you.


